Dollar index investing means profiting from changes in the USD’s strength relative to foreign currencies. This article explains the basics, strategies, and factors any investor and trader needs to know about the US dollar index.
Key Takeaways
- The U.S. Dollar Index measures the strength of the USD against a basket of six major currencies, with the euro having the most significant influence. Reading above 100 levels signals, that US dollar strengthened vs the currencies in the basket, while below 100 signals that US dollar is weaker than currencies cumulative power
- Key factors affecting the Dollar Index include Federal Reserve policies, economic indicators, and global events, which can lead to substantial fluctuations - weakening (recessions, large US - Europe bond yield spreads, financial crises or even higher risk appetite) or strengthening US dollar (high oil prices, strong macro data, higher inflation, lower risk appetite)
- Investors can utilise dollar index futures and various trading strategies, such as fundamental and technical analysis, to enhance their investment decisions and manage risks. US Dollar index (so-called DXY) derivatives (such as USDIDX) are objects of global market trades and speculators.
Dollar index investing means profiting from changes in the USD’s strength relative to foreign currencies. This article explains the basics, strategies, and factors any investor and trader needs to know about the US dollar index.
Key Takeaways
- The U.S. Dollar Index measures the strength of the USD against a basket of six major currencies, with the euro having the most significant influence. Reading above 100 levels signals, that US dollar strengthened vs the currencies in the basket, while below 100 signals that US dollar is weaker than currencies cumulative power
- Key factors affecting the Dollar Index include Federal Reserve policies, economic indicators, and global events, which can lead to substantial fluctuations - weakening (recessions, large US - Europe bond yield spreads, financial crises or even higher risk appetite) or strengthening US dollar (high oil prices, strong macro data, higher inflation, lower risk appetite)
- Investors can utilise dollar index futures and various trading strategies, such as fundamental and technical analysis, to enhance their investment decisions and manage risks. US Dollar index (so-called DXY) derivatives (such as USDIDX) are objects of global market trades and speculators.
Understanding the US Dollar Index

Source: Adobe Stock Images
The U.S. Dollar Index (USDX) is a critical tool for investors and traders alike. Created in 1973, now it serves as a benchmark for evaluating the USD’s strength against a basket of six major foreign currencies: The euro, Japanese yen, British pound, Canadian dollar, Swedish krona, and Swiss franc.
This index reflects the dollar’s value in international markets, providing a clear picture of its performance relative to other currencies. Knowing the calculation, historical performance, and influencing factors of the dollar index aids in making better investment choices.
What is the Dollar Index?
The dollar index measures the USD’s worth against a basket of six major foreign currencies, with the euro accounting for approximately 57.6% of the index, making it the most influential currency within the index. It serves as an important indicator for traders and investors to assess the strength of the dollar in comparison to its counterparts, influenced by key economic metrics such as GDP growth, employment rates, and inflation trends.
How to Calculate the Dollar Index
The dollar index is calculated using a weighted geometric mean of the USD’s exchange rates against multiple currencies. The calculation method allows traders and investors to assess the strength of the US dollar against a global currency basket, influencing trading and investment decisions.
Also, the US dollar index is tracked by traders, which are betting on macro changes, central banks decisions and bond yields spreads across the major economies. Historical trends can provide valuable context for using technical analysis to predict future movements and guide investment decisions.
Historical Performance
Since its creation in 1973, the dollar index has seen significant fluctuations, peaking at nearly 165 in 1984 and reaching a low of about 70 in 2007. The US dollar weakened after Covid-19 panic, which pressured Fed to be extremely dovish, but rebounded strongly in 2022 as Fed started to fight with spreading inflation, rising interest rates to the highest level in decades. We can assume that the Federal Reserve stance is probably the most important factor for the US Dollar index.
Key Factors Affecting the Dollar Index

Source: Adobe Stock Images
Several key factors influence the dollar index, including Federal Reserve policies, economic indicators, and global events and geopolitics. These factors can cause significant fluctuations in the index, impacting international trade and investment flows.
Federal Reserve Policies
The Federal Reserve’s decisions on interest rates and monetary policy play a crucial role in determining the strength of the USD. When the Federal Reserve raises the federal fund rate, it generally leads to an increase in interest rates across the economy, boosting the dollar’s appeal to foreign investors.
Changes in the Federal Reserve’s interest rates can greatly affect the dollar’s strength, as higher rates generally attract international investment and US dollar inflows. On the other hand, lower interest rates impact treasuries yields and US dollar negatively.
Economic Indicators
Economic indicators such as GDP growth, employment rates, and the trade balance significantly affect the dollar index. For instance, a positive trend in employment figures typically strengthens the dollar, while a trade deficit generally leads to a weaker dollar due to higher demand for foreign currencies.
When the dollar weakens, it can further exacerbate the trade deficit. What’s more, weaker economic data usually lead to dovish Fed response (lowering rates or using other policy tools such as QE and so on). Finally, dovish Fed policy may be negative for the US dollar purchasing power.
Global Events and Geopolitics
Global events and geopolitical risks play a significant role in currency markets, leading to volatility and influencing indices such as the dollar index. For example, the Japanese yen, considered a safe-haven currency, can lead to increased volatility in the dollar index during periods of economic uncertainty.
Uncertainty across the US economic conditions, as well as financial crises or other global events such as pandemic, may weaken the US dollar. On the other hand, geopolitical tensions, higher oil prices or wars may lead to strengthening (so-called weaponising) the US dollar.
USD Index, Fed Funds Rate and 10y US Treasury Bond Yields
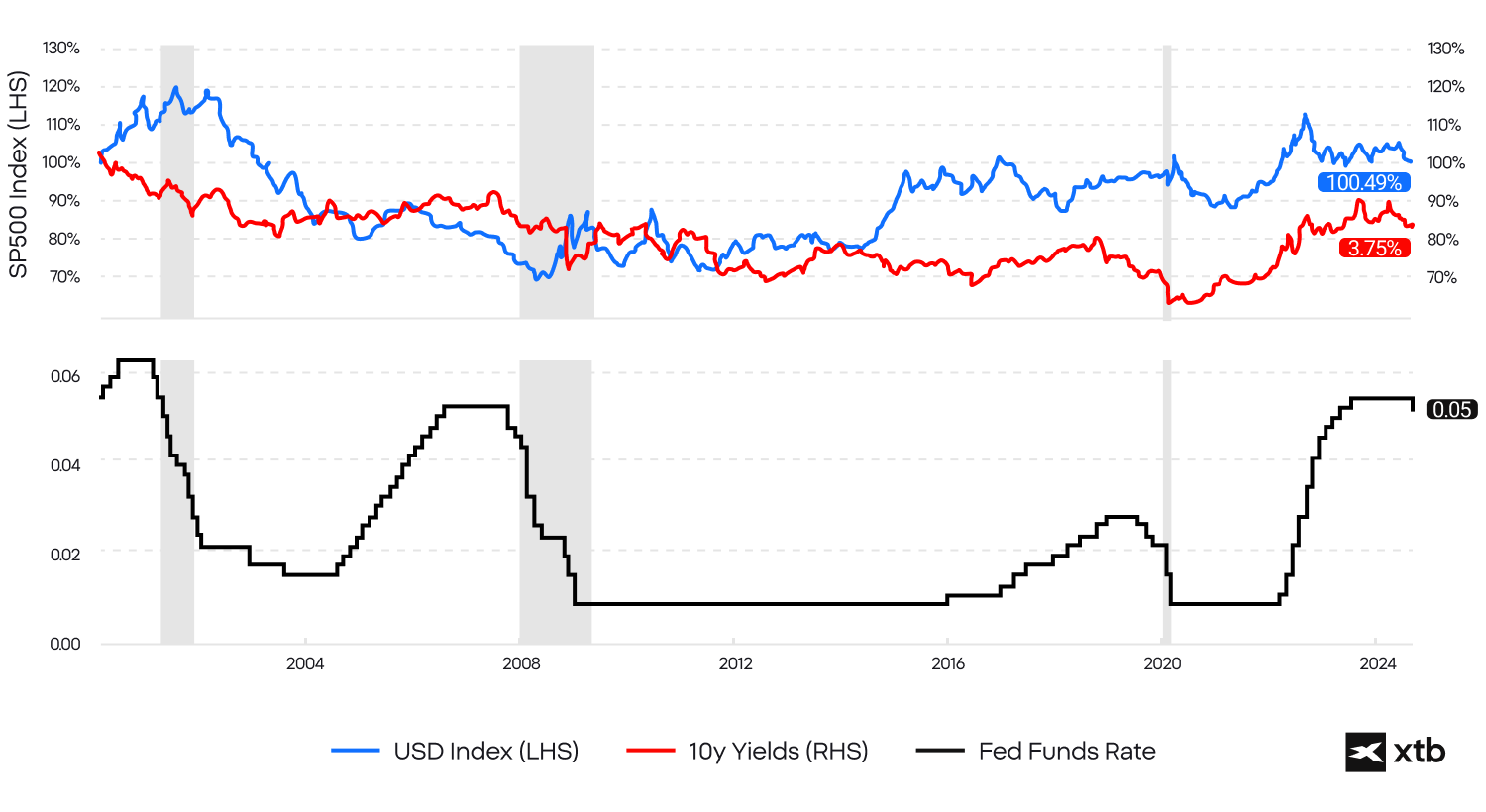
As we can see, there is a clear correlation between the US Dollar Index, 10-year yields and Fed Funds Rate over the last 20 years. If Fed interest rates drop, also yields are lower, pressuring the USD Index. However, remember that the past cannot be an indicator of future results. Source: XTB Research, Bloomberg Finance L.P.
The Fed Role

Source: Adobe Stock Images
The Federal Reserve (Fed) plays a crucial role in influencing the U.S. Dollar Index. The Fed primarily impacts the dollar through its interest rate decisions. But how and why? Here is the highlight.
The easy example
Imagine the U.S. dollar as a product on a store shelf. When the Fed raises interest rates, it’s like putting a “limited edition” sticker on that product. This attracts investors because higher rates mean better returns on U.S. investments, making the dollar more valuable. As a result, the demand for dollars increases, causing the US dollar index to rise, indicating a stronger performance against other currencies (especially if the spread between monetary policy is huge).
On the flip side, when the Fed cuts interest rates, it’s like putting a “discount” sticker on the dollar. Lower rates make U.S. investments less attractive because the returns are smaller. This can decrease demand for the dollar, leading to a weaker dollar and a lower USDX. For example, even anticipation of Fed rate cuts weakened the dollar in advance, as investors expected lower returns from U.S. assets, pushing the USDX down.
When the Fed cuts interest rates, it makes borrowing cheaper, which generally leads to a weaker dollar. Lower rates reduce returns on investments denominated in dollars, making them less attractive to investors. This can result in a shift of capital away from the U.S., putting downward pressure on the dollar’s value.
Even the anticipation of rate cuts has contributed to a weakening dollar, as investors adjust their expectations for future returns. The magnitude of the rate cut — whether small or large — can further influence the direction of the dollar, as larger cuts might lead to a more pronounced decline.
On the other hand, when the Fed raises rates, it increases the return on dollar-denominated assets, attracting foreign investment and strengthening the dollar. A strong dollar benefits those travelling or buying foreign goods but can make U.S. exports more expensive, potentially hurting domestic manufacturers.
Fed policy tools impacting US dollar index
The US Federal Reserve has a few monetary policy tools, which (if used) - impact the US dollar directly. Here are the major 3 of them.
Interest Rate Decisions
- Raising rates makes the dollar stronger, as higher returns attract investors.
- Lowering rates weakens the dollar by making it less attractive.
Quantitative Easing (QE) and Tightening (QT)
- QE (buying bonds) increases money supply, weakening the dollar.
- QT (selling bonds) reduces money supply, strengthening the dollar.
Forward Guidance
- So-called hawkish guidance, when the Fed signals future rate hikes or tightening, the dollar often strengthens, as US treasury bonds yields rise
- So-called dovish guidance (lower rates or easing) can weaken the dollar and US treasury bonds.
Positive for the U.S. Dollar
- Interest Rate Hikes: Raising interest rates makes U.S. assets more attractive, increasing demand for the dollar and boosting its value.
- Open Market Operations (OMOs): The Fed can buy U.S. government securities, reducing the money supply, which can support the dollar by keeping inflation in check and making U.S. investments more appealing.
- Reverse Repurchase Agreements (Reverse Repos): These transactions help manage short-term interest rates and can indirectly strengthen the dollar by tightening financial conditions.
Negative for the U.S. Dollar
- Interest Rate Cuts: Lowering rates reduces returns on U.S. investments, making the dollar less attractive and weakening it.
- Quantitative Easing (QE): The Fed buys long-term securities, increasing the money supply, which can devalue the dollar by increasing inflationary pressures.
- Dovish Forward Guidance: Communicating plans to keep rates low can also weaken the dollar by shaping market expectations towards easier monetary conditions
Impact of other currencies on the Dollar Index

Adobe Stock Images
The U.S. Dollar Index is primarily influenced by major currencies such as the euro. However, understanding the impact of all currencies can help investors anticipate movements in the dollar index and make strategic investment decisions.
Euro's Influence
The euro is one of the most significant currencies in relation to the US dollar, accounting for a large percentage of the dollar index. Economic conditions in the Eurozone, such as growth rates and interest rates, directly affect the euro’s value, thereby influencing the dollar index. Historical performance data shows that fluctuations in the euro often correlate with significant movements in the dollar index, sometimes reflecting past trends.
The difference between the European Central Bank and US Federal Reserve stance may impact the index. For example, when the Fed is extremely hawkish (for example solid economic growth and inflation risks), while ECB is dovish (for example recession, low inflation), the US Dollar may gain. However, if this dynamic changes, with the Fed lowering rates - the US dollar index may fall.
Japanese Yen and Its Effects
The Japanese yen makes up 13.6% of the Dollar Index. Shifts in the value of the Japanese yen can affect the dollar index, although its impact is less pronounced compared to the euro. In general, the hawkish Bank of Japan stance may pressure the US Dollar Index.
Especially if stronger economic progress, higher inflation and wages growth in Japan pressure the BoJ to change its extremely dovish policy for decades. The yen significantly influences the dollar index dynamics due to its contribution among other currencies. This dynamic may also hit so-called “carry trade” strategies.
Emerging Market Currencies
Emerging market currencies are increasingly influential in shaping the dynamics of the dollar index, reflecting their growing economic relevance and trading volumes. As economies in emerging markets grow, their currencies start to play a more significant role in international trade and investment, impacting the valuation of the dollar index. Also, China’s yuan has gained significant traction in global markets, and may have increased its influence on the dollar index.
Investing and Trading US dollar index

Adobe Stock Images
Investing in the dollar index can be approached through various methods. Those include direct and risky investment in dollar index CFDs such as USDIDX or dollar related ETFs such as PIMCO US Dollar Short Maturity UCITS.
- Identifying clear investment goals and risk tolerance is vital before entering the dollar index market. Staying updated with relevant financial news, central bank decisions and economic indicators is essential for making informed dollar index investment decisions.
- Setting investment goals for the dollar index includes determining desired returns, time frames, and acceptable risk levels. Goals should consider specific time horizons and risk tolerance for dollar index investments. Both traders and investors should be aware that the past is not an indicator of future returns.
Choosing the Right Instruments
Performance metrics and benchmarks are essential for tracking the success of dollar index investments. Various tools and trading platforms can help analyse these metrics. It’s common that traders are usually more interested in leveraged, risky products such as CFDs, while investors are looking for more medium and long term ‘bets’, such as ETFs.
Managing Risks
Traders often employ hedging strategies using Dollar Index Futures to offset risks associated with specific currency positions. One common strategy involves using dollar index futures to hedge against currency risk when trading other international assets. Risk management is vital for successful dollar index investments, given market volatility.
Tracking Performance and Strategies Adjustment
Monitoring the US Dollar Index (USDX) is crucial for assessing the dollar’s strength against other currencies. The dollar index tracks its performance, which is essential for informed financial decisions. Timely strategy adjustments enhance the resilience of dollar index investments amid changing market conditions. These adjustments help navigate volatility and shifting market dynamics.
Staying Informed
Macro investors and traders should track global economic conditions and interest rates decisions, especially from the Fed. Staying informed about the US dollar index is vital as it influences investment strategies and market decisions, related to its dynamics. Reliable information sources include analysts news sections inside the trading platforms, financial news sites, economic reports, and central bank releases. Any new alert can provide timely updates on significant changes.
Dollar Index Futures
Dollar index futures are financial contracts that allow traders to speculate on the value of the USD against a basket of foreign currencies. These futures provide a mechanism for managing currency exposure and hedging against potential adverse movements in the dollar’s value. Traders also have the option to directly trade the US Dollar Index using derivatives like CFDs, such as USDIDX.
Trading Strategies
Common trading strategies with dollar index futures include going long when expecting dollar strength and shorting when anticipating a decline. Utilising CFDs allows traders to speculate on price movements of the US Dollar Index without the need to own the underlying asset. However, leveraging increased potential risks, leading to substantial losses.
Risks and Rewards
Trading dollar index futures involves various risks, including market risk, credit risk, and liquidity risk. Market volatility can significantly impact the value of dollar index futures, leading to potential losses for traders. However, successful trading of these products can lead to considerable profits, particularly during periods of favourable (depending on each trader position) economic conditions.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis aids investors in making informed decisions about the dollar index by examining historical price data and trading volumes to predict potential trends. Understanding technical indicators and price dynamics can impact investment approaches.
Key Technical Indicators
Moving Averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Bollinger Bands are common technical indicators that help gauge market momentum and potential reversals. These tools are vital for analysing the dollar index and assisting traders in making informed decisions. Using these technical indicators allows traders to assess market conditions and make strategic decisions.
Chart Patterns
Chart patterns such as head and shoulders, double tops, and triangles can indicate bullish or bearish market sentiments regarding the Dollar Index. Understanding these patterns may help predict potential fluctuations in the dollar index. However, there is no confirmed efficiency in technical analysis methods; there is no such technical formation which can predict future outcomes.
Summary
The US dollar index is one of the most important market sentiment benchmarks, reflecting the power of the US Dollar vs other major economies such as the Eurozone or Japan. When the US Dollar weakens (it may be multiple reasons such as recessions, Fed rate cuts and so on), the US Dollar index usually also falls. The index usually rises, when the Fed is hiking interest rates to trim inflation risks. Trading the dollar index requires a comprehensive understanding of various factors, from the fundamentals of the index itself to the influences of global events and technical analysis.
FAQ
The Dollar Index is a benchmark that measures the value of the U.S. dollar against a basket of six major foreign currencies, indicating its strength in global markets.
The Dollar Index is calculated as a weighted geometric mean of the U.S. dollar's exchange rates against a basket of currencies, where the euro holds the largest weight at 57.6%. This methodology reflects the dollar's value in relation to major foreign currencies.
The Dollar Index is primarily influenced by Federal Reserve policies, key economic indicators, and significant global events. Understanding these factors is essential for analysing currency fluctuations effectively.
Dollar Index Futures are contracts that enable traders to speculate on the value of the U.S. dollar relative to a group of foreign currencies, thus facilitating the management of currency exposure. They serve as an important tool in the foreign exchange market.
To effectively manage risks when investing in the Dollar Index, consider employing hedging strategies like Dollar Index Futures to offset currency position risks, and ensure you regularly monitor and adjust your investment strategies.

Understanding Forex Volatility: Causes, Effects, and Strategies

Investing in Currencies

The Israel-Iran conflict explained and its effect on the global markets
This content has been created by XTB S.A. This service is provided by XTB S.A., with its registered office in Warsaw, at Prosta 67, 00-838 Warsaw, Poland, entered in the register of entrepreneurs of the National Court Register (Krajowy Rejestr Sądowy) conducted by District Court for the Capital City of Warsaw, XII Commercial Division of the National Court Register under KRS number 0000217580, REGON number 015803782 and Tax Identification Number (NIP) 527-24-43-955, with the fully paid up share capital in the amount of PLN 5.869.181,75. XTB S.A. conducts brokerage activities on the basis of the license granted by Polish Securities and Exchange Commission on 8th November 2005 No. DDM-M-4021-57-1/2005 and is supervised by Polish Supervision Authority.


