Unfortunately, tensions in the eastern Ukraine escalated following the end of the Winter Olympics in Beijing. While it is too soon to speak about an outright invasion, Russia has violated Ukrainian borders by moving its military into newly-recognized republics in Donbas region. Another part of Ukraine was annexed by Russia. In-line with earlier announcements, European and US leaders imposed sanctions. However, they will have to go much further in order to tame Putin's ambitions.
What sanctions have been announced already?
List of sanctions announced by the United States, European Union, Canada, Japan and the United Kingdom is long. However, just as it was the case in 2014, most of those sanctions will not have a material impact on the Russian economy. Some of them, like EU personal sanctions on Russian parliament members or US ban on investments in Donetsk and Luhansk, are largely symbolic. Halt of Nord Stream 2 certification is the biggest on the list but as Germany did not rule out completely abandoning the project, it cannot be ruled out that halt will be lifted sooner or later. Sanctions on Russian banks were also levied but did not target the biggest state lenders - Sberbank or VTB Bank. Russian government and state agencies had their access to financial markets limited. However, this should not be big of an issue for Moscow given low Russian debt. So far, sanctions were not as severe and some kind of a relief can be spotted in the financial markets. Investors view the situation as a repeat of the 2014 situation, when sanctions had little impact and Russia was allowed to keep its war spoils.
What potential sanctions could still be announced?
It goes without saying that if the West wants to stop Putin's ambitions, it would need to go further than already announced sanctions. However, more severe actions against Russia would also have a negative impact on countries imposing them. So far, Western leaders are reluctant to impose such sanctions. What could they be?
Halt to energy imports from Russia would be the biggest hit to the Russian economy. Of course, such a move is not even being considered. European Union is more afraid that it would be Moscow that decides to halt energy exports to EU, pushing energy price in Europe even higher. This is also the reason why EU is reluctant to impose sanctions on Russia's access to SWIFT payments system. There is some chatter in the United States on banning technology sales to Russia. However, in such a scenario, Russia could look towards Chinese technology. Sanctions on largest banks could also be announced but the West is concerned how it would impact its investments in Russia. As one can see, any steps that would result in a bigger hit to the Russian economy would also mean negatively impacting Western economies.
Oil and natural gas are drivers of Russian economy
Europe cannot halt energy imports from Russia but NATO countries can carry out energy policy that will negatively impact Russia rather than help it. It should be noted how big was a drop in Russian energy revenues in 2015-2017, what had a bigger impact on Russian economy than sanctions imposed in the aftermath of the Crimea Annexation. What were the reasons? Firstly, huge expansion of the US shale sector that change oil market balance and barred OPEC and Russia from lifting oil prices. Sadly, OPEC+ has regained its price setting power. It should be pointed out that climate policy should be long-term negative for Russia but is positive in the short-term as it leads to lower production in the US and higher demand in Europe.
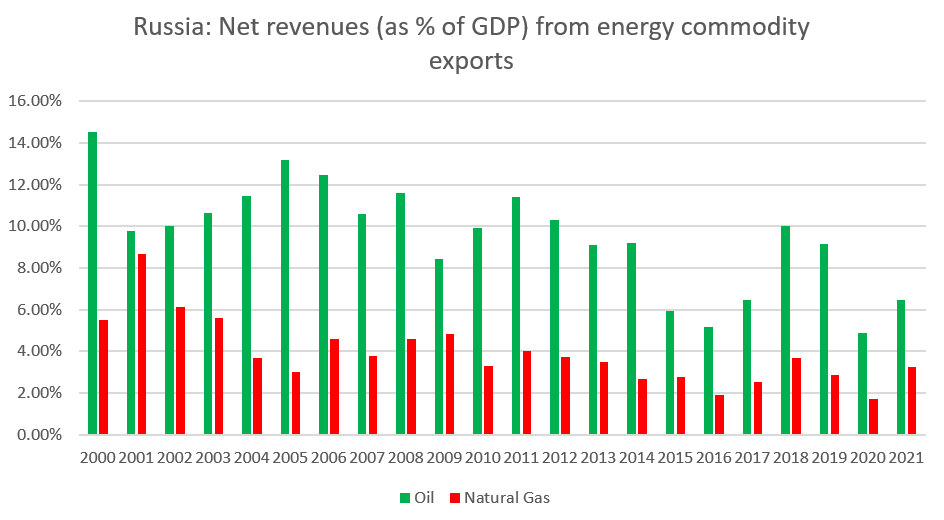
Russian net revenues from natural gas and oil exports accounted for as much as 20% in some of the year! Source: Bloomberg, WorldBank, XTB Research
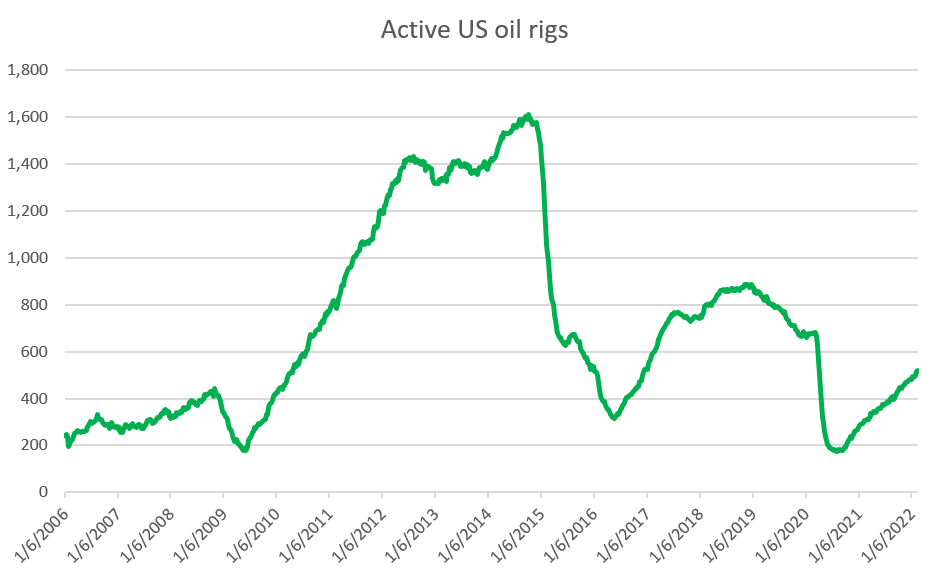
Number of active oil rigs in the US is recovering but remains at very low levels. Source: Baker Hughes
Long-term view needed
What should be done then? United States should support its own oil sector, as well as oil sector in allied countries (Mexico, Brazil), and reach an agreement with Iran as quickly as possible. Europe should act to reduce its dependence on Russian energy imports. Effective sanctions on Moscow cannot be levied if they do not target Russian energy exports. Without such actions, Russian hunger for more land may never be satisfied. Risk of further escalation will weigh on markets and can lift fuel prices even higher.
 OPEC control over the oil market is doing more to push prices higher than geopolitics. Such a situation is benefitting Moscow. Source: xStation5
OPEC control over the oil market is doing more to push prices higher than geopolitics. Such a situation is benefitting Moscow. Source: xStation5

NATGAS slides 6% on shifting weather forecasts

The Week Ahead

Three markets to watch next week (09.02.2026)

Market update: recovery takes hold, but investors remain on edge
This content has been created by XTB S.A. This service is provided by XTB S.A., with its registered office in Warsaw, at Prosta 67, 00-838 Warsaw, Poland, entered in the register of entrepreneurs of the National Court Register (Krajowy Rejestr Sądowy) conducted by District Court for the Capital City of Warsaw, XII Commercial Division of the National Court Register under KRS number 0000217580, REGON number 015803782 and Tax Identification Number (NIP) 527-24-43-955, with the fully paid up share capital in the amount of PLN 5.869.181,75. XTB S.A. conducts brokerage activities on the basis of the license granted by Polish Securities and Exchange Commission on 8th November 2005 No. DDM-M-4021-57-1/2005 and is supervised by Polish Supervision Authority.


