This article provides readers with a comprehensive guide of everything you need to know on spread betting. It examines topics such as bid and ask prices, what financial instruments you can invest in and all the risks involved.
This article provides readers with a comprehensive guide of everything you need to know on spread betting. It examines topics such as bid and ask prices, what financial instruments you can invest in and all the risks involved.
We also explore techniques for how spread betting works, the tax implications and how it differs from traditional trading. So for those looking for responsible ways to start spread betting, continue reading to uncover how a comprehensive guide can pave the way for achieving success.
What Is Spread Betting?
Spread betting is a financial trading strategy that allows individuals to speculate on the price movements of various financial instruments, such as stocks, indices, currencies, commodities, and more. It's a form of derivative trading where the trader does not own the underlying asset but instead bets on whether the price of the asset will go up or down. The profit or loss in spread betting is determined by the accuracy of the trader's prediction.
How Does Spread Betting Work?
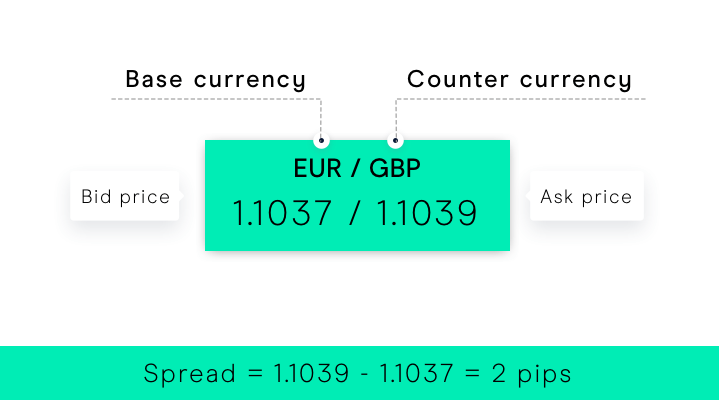
You start by choosing an asset. A trader usually selects a financial instrument they want to trade, such as a stock, currency pair, or commodity. In spread betting, there are two prices quoted for each asset. The bid price (sell price) and the ask price (buy price). The difference between these two prices is called the "spread." That is when a trader decides whether they think the price of the chosen asset will rise (go long) or fall (go short). If they believe the price will rise, they place a bet at the ask price. If they believe the price will fall, they place a bet at the bid price.
Traders place a stake per point or per pip. If you are not familiar with the terms, a point or pip is the smallest price movement in the asset's value. The stake represents how much money the trader is betting per point movement in the asset's price.
You then have to calculate the profit or loss which is calculated based on the difference between the closing price of the asset and the price at which the bet was opened, multiplied by the stake. If the trader's prediction is correct and the price moves in the anticipated direction, they make a profit. If the price moves against their prediction, they incur a loss.
Every trader should know that spread betting often involves leverage, which allows traders to control a larger position with a smaller amount of capital. While leverage can amplify profits, it also magnifies potential losses.
Many spread betting platforms offer risk management tools such as stop-loss and take-profit orders. These tools help traders limit potential losses and secure profits by automatically closing positions at specified price levels.
Understanding the Bid and Ask Prices?
Bid and ask prices are fundamental concepts in trading, including spread betting. They represent the prices at which you can buy and sell a particular financial instrument. Bid Price also known as the Sell Price is the price at which the market is willing to buy a specific financial instrument from you. If you're looking to sell a spread bet or any other financial asset, the bid price is the price you would receive if you were to sell right at that moment. Traders who believe the price of the asset will decrease often use the bid price for their transactions.
Ask Price known as the Buy Price is the price at which the market is willing to sell a specific financial instrument to you. If you're looking to buy a spread bet or any other financial asset, the ask price is the price you would need to pay if you were to buy right at that moment. Traders who believe the price of the asset will increase often use the ask price for their transactions.
As mentioned above, the difference between the bid and ask prices is known as the "spread."
For example, let's say you're betting on a stock. The bid price might be $50, and the ask price might be $51. In this case, if you want to go short (betting that the price will fall), you would sell at the bid price of $50. If you want to go long (betting that the price will rise), you would buy at the ask price of $51.
The bid and ask prices can fluctuate rapidly based on market supply and demand, news, economic data, and other factors. It's essential to consider these prices when placing trades, as they directly impact your potential profit or loss.
How Does Spread Betting Differ From Traditional Trading?
Both spread betting and traditional trading have their advantages and risks. Spread betting is often favoured by short-term traders who want to capitalise on small price movements without owning the underlying asset.
Let's get into it in a bit more detail:
Ownership of Assets:
- In traditional trading, you actually own the underlying asset (e.g., stocks, bonds, commodities) that you buy or sell.
- With spread betting, you do not own the underlying asset. Instead, you are speculating on the price movement of the asset without directly owning it.
Regulation:
- Traditional trading is subject to financial regulations and oversight from various authorities.
- Spread betting is also subject to regulations, but the rules might differ from those governing traditional trading. Spread betting providers are regulated by financial authorities in their respective jurisdictions.
Profit from Price Movements:
- In traditional trading, you profit by buying an asset at a lower price and selling it at a higher price.
- In spread betting, you profit based on the accuracy of your prediction about whether the price of the asset will go up (long) or down (short). You gain or lose based on the difference between the opening and closing prices of the bet.
Leverage:
- Leverage is available in traditional trading but might be subject to more regulatory restrictions and margin requirements.
- Spread betting frequently involves higher leverage, allowing traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital. This can amplify both profits and losses.
Tax Treatment:
- The tax treatment of gains and losses from traditional trading can vary depending on the jurisdiction and the asset class. Capital gains taxes might apply.
- In some jurisdictions, spread betting is treated differently for tax purposes. In certain countries, spread betting profits may be tax-free. However, tax regulations can vary, so it's essential to understand the rules in your specific location.
Short Selling:
- Short selling involves borrowing an asset and selling it with the intention of buying it back at a lower price.
- Spread betting inherently involves speculation on both rising and falling prices, so you can easily place bets on assets you believe will decrease in value.
Range of Assets:
- Traditional trading encompasses a wide range of assets, including stocks, bonds, commodities, and more.
- Spread betting platforms offer a variety of assets, but the range might differ from traditional trading. Some platforms focus on specific asset classes.
Accessibility:
- Traditional trading often requires a brokerage account, and the process can involve more paperwork and regulations.
- Spread betting can be more accessible as it often involves opening an account with a spread betting provider. The process may be more streamlined and geared toward active traders.
What Financial Instruments Can I Spread Bet On?
Here are some common types of financial instruments that you can typically spread bet on:
Stocks and Equities:
- You can spread bet on individual company stocks. This allows you to speculate on whether the stock's price will rise or fall without owning the actual shares.
Indices:
- Spread betting on indices involves speculating on the overall performance of a group of stocks representing a specific market or sector. Examples include the FTSE 100, S&P 500, and DAX.
Currencies (Forex):
- Spread betting on currency pairs involves speculating on the exchange rate between two currencies, such as EUR/USD or GBP/JPY.
Commodities:
- Commodities like gold, silver, oil, and agricultural products can be spread bet on. You speculate on the future price movement of these physical assets.
Bonds:
- You might have the opportunity to spread bet on government bonds or other fixed-income securities.
Interest Rates:
- Speculating on interest rates involves predicting how central banks might adjust interest rates, which can impact various financial markets.
Options and Derivatives:
- In some cases, spread betting platforms offer options and other derivative products for speculation.
Sectors and Industries:
- You can also find options to spread bet on specific sectors or industries within the stock market, such as technology, healthcare, or energy.
Market Indices and ETFs:
- You can spread bet on various market indices and Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs).

What Are the Tax Implications of Spread Betting?
The tax implications of spread betting can vary significantly depending on your jurisdiction and local tax laws. In some countries, spread betting may offer certain tax advantages, while in others, it might be subject to taxation like any other form of income or investment.
In the UK and Ireland, according to HM Revenue & Customs profits from spread betting are often tax-free, from both Stamp Duty and Capital Gains Tax (CGT),as they are considered gambling winnings rather than investment gains. This means you don't need to report either capital gains tax or income tax on your spread betting profits to HMRC.
However, every trader should note that in some countries, spread betting is treated as a financial trading activity and is subject to taxation. Profits may be considered taxable income or subject to capital gains tax, depending on the local tax laws.
In jurisdictions where spread betting is considered gambling, losses from spread betting might not be tax-deductible. However, in countries where spread betting is treated as trading, losses may be offset against other trading profits for tax purposes.
If you engage in frequent spread betting activities, you might be classified as a day trader. In some places, day trading can have specific tax implications, including different tax rates or reporting requirements.
Tax treatment can also vary based on the type of financial instrument you're spread betting on. Some countries might treat forex spread betting differently from spread betting on stocks or indices.
Your individual tax situation, including your total income, tax brackets, and other investments, can influence the tax treatment of spread betting profits. Tax laws can change, so it's important to stay informed about any updates or amendments to tax regulations that might affect your spread betting activities.
Given the complexity and variability of tax regulations, it's strongly recommended to consult a qualified tax professional who is familiar with the tax laws in your jurisdiction. They can provide accurate guidance based on your specific circumstances and local regulations. This will help ensure that you understand your tax obligations related to spread betting and can make informed decisions.
For more information, please visit the official website of HMRC.
What Are the Risks of Spread Betting?
Spread betting, like any form of trading, involves a range of risks that traders should be aware of before engaging in this activity. Spread betting involves the potential for significant losses. Since profits and losses are determined by the size of the price movement, it's possible to lose more than your initial stake.
While leverage can amplify profits, it also magnifies losses. With relatively small price movements, leveraged positions can result in substantial gains or losses.Financial markets can be highly volatile, leading to sudden and unpredictable price movements. These fluctuations can result in rapid gains or losses. Traders have limited control over market events. Unexpected news, economic data releases, or geopolitical events can influence markets and impact positions too.
The accessibility and fast-paced nature of spread betting can lead to overtrading, where traders make excessive trades without proper analysis. This can result in increased losses. Traders who are not fully familiar with the specific instruments they are spread betting on can make incorrect predictions and incur losses.
Final Thoughts
As we discussed above, it's important for traders to have a clear understanding of the market, the assets they're trading, and the risks involved. Many traders use spread betting as a way to speculate on short-term price movements and engage in active trading, but it requires careful research, risk management, and discipline.
To mitigate these risks, traders should educate themselves thoroughly about spread betting, the specific instruments they're trading, and the markets they're participating in. Developing a solid trading strategy with clear entry and exit rules will help too. By setting stop-loss and take-profit levels you can manage risk. Use leverage cautiously and be aware of its impact on positions. Start with a demo account to practise without real money and only trade with capital you can afford to lose.
Remember that no trading strategy guarantees profits, and losses are a natural part of trading. It's crucial to manage your risk effectively and approach spread betting with a disciplined and informed mindset.
Please note, XTB does not offer spread betting.
FAQ
Spread Betting is a form of derivative trading where you speculate on the price movements of various financial instruments without owning the underlying assets.
While Spread Betting can be accessible, beginners should educate themselves, start with a demo account, and gradually transition to real trading.
Both involve speculating on price movements, but Spread Betting is often tax-efficient and popular in the UK, while CFDs have broader global use.
Potential for profit in rising and falling markets, leverage, tax advantages in certain jurisdictions, and flexibility in trading different assets.
Risks include loss of capital, leverage amplification, market volatility, counterparty risk, and psychological factors.

Bull Market vs Bear Market: What's The Difference?

Hawkish Vs Dovish: Differences Between Monetary Policies Explained

Bull and Bear Markets - Everything You Need To Know
This content has been created by XTB S.A. This service is provided by XTB S.A., with its registered office in Warsaw, at Prosta 67, 00-838 Warsaw, Poland, entered in the register of entrepreneurs of the National Court Register (Krajowy Rejestr Sądowy) conducted by District Court for the Capital City of Warsaw, XII Commercial Division of the National Court Register under KRS number 0000217580, REGON number 015803782 and Tax Identification Number (NIP) 527-24-43-955, with the fully paid up share capital in the amount of PLN 5.869.181,75. XTB S.A. conducts brokerage activities on the basis of the license granted by Polish Securities and Exchange Commission on 8th November 2005 No. DDM-M-4021-57-1/2005 and is supervised by Polish Supervision Authority.


