US CPI Inflation for August 2024: Market expectations
- Market consensus points to an increase in monthly and core monthly inflation at 0.2% m/m, similar to the previous month. Such a change on a monthly basis is desirable for the Fed looking at the prospect of reaching its inflation target by the forecast deadline
- On an annual basis, inflation is expected to fall to 2.5% for August, down from 2.9% y/y in July. The CPI Core inflation is expected to remain stable at 3.2% y/y, the same as in July reading.
Inflation data for August will likely show that companies are beginning to struggle to pass on higher costs to consumers, further curbing inflation. Companies in the face of this are looking to cut costs with employees, resulting in less hiring or even layoffs. Core inflation, which is key from the Fed's perspective, is likely to remain stable, which in theory leaves the door open for a larger interest rate cut. On the other hand, its level is far from the inflation target, so a 25 basis point interest rate cut still seems to be the base scenario.
CPI Core and PPI Core inflation did not respond to the significant increase in transportation costs recently. This may indicate that demand is weakening, resulting in an inability to put the costs fully to consumers, reducing companies margins. Source: Bloomberg Finance LP, XTB
Looking at the various components of inflation, it is worth noting that real estate inflation, specifically rents and their equivalents, continues to weigh most heavily. In this regard, based on the Case Shiller index, we should still see a decline in the share of this inflation in the next few months.
- Used cars have recently been one of the factors pulling inflation down. Nonetheless, it is worth noting that the year-on-year decline in prices as measured by the Manheim index is beginning to abate. However, it is still a year-on-year decline. The same situation exists in terms of food prices, based on the FAO food index. On a monthly basis, however, prices are rebounding.
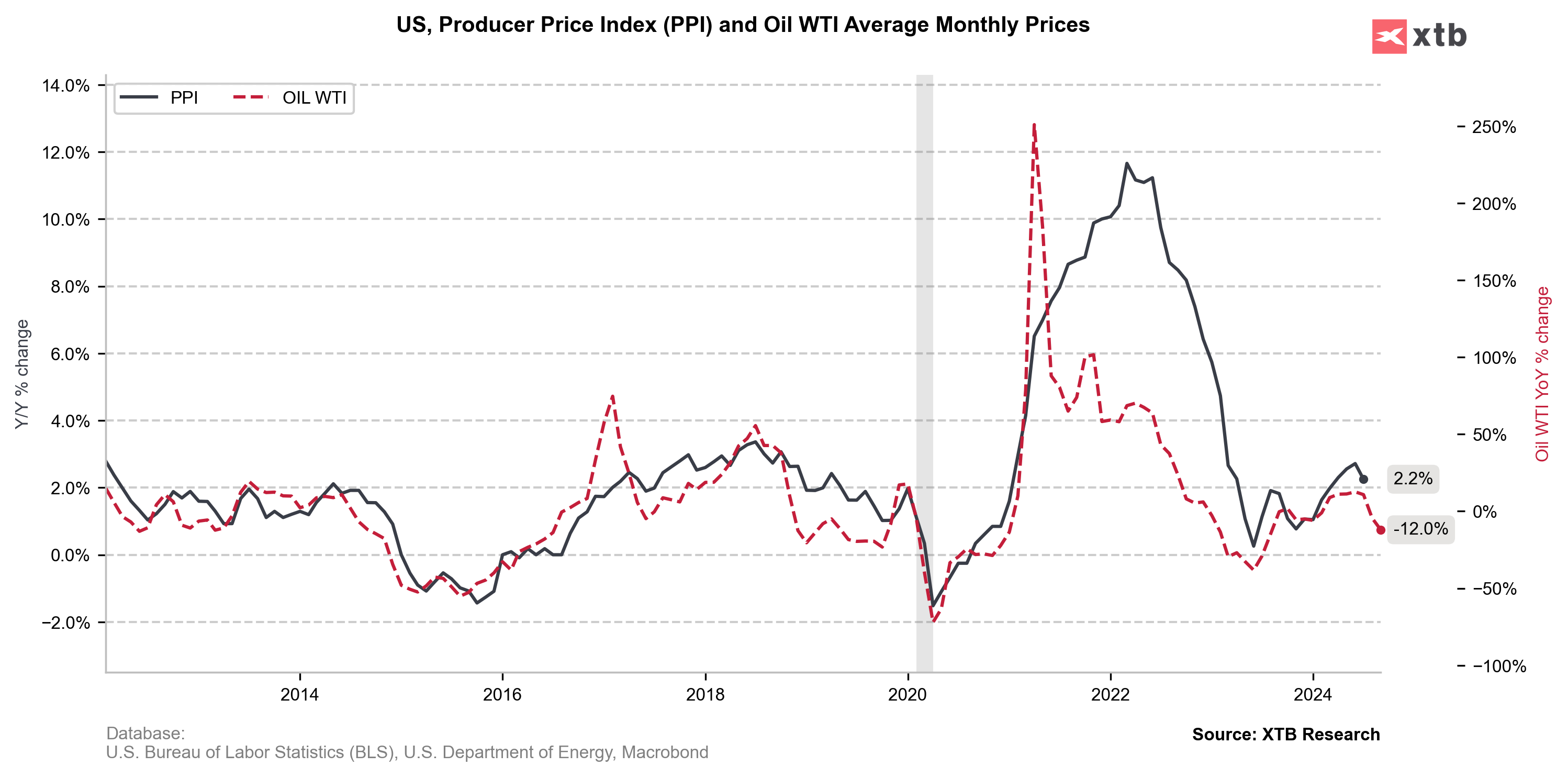
- One of the more important factors that should lead to a decline in overall inflation is the price of oil and gasoilne, which fell sharply in August and is likely to continue falling for September. It is also worth noting that for August we had a significant drop in wage growth to 3.6%. The 3% level is in line with the inflation target of 2%. In view of this, there is no pressure from demand for a rebound in core inflation.
![]()
Oil prices could have quite an impact on curbing inflation in the near term, which would justify interest rate cuts. The question is whether inflation will fall enough to support 50 bps Fed cuts? Source: Macrobond, XTB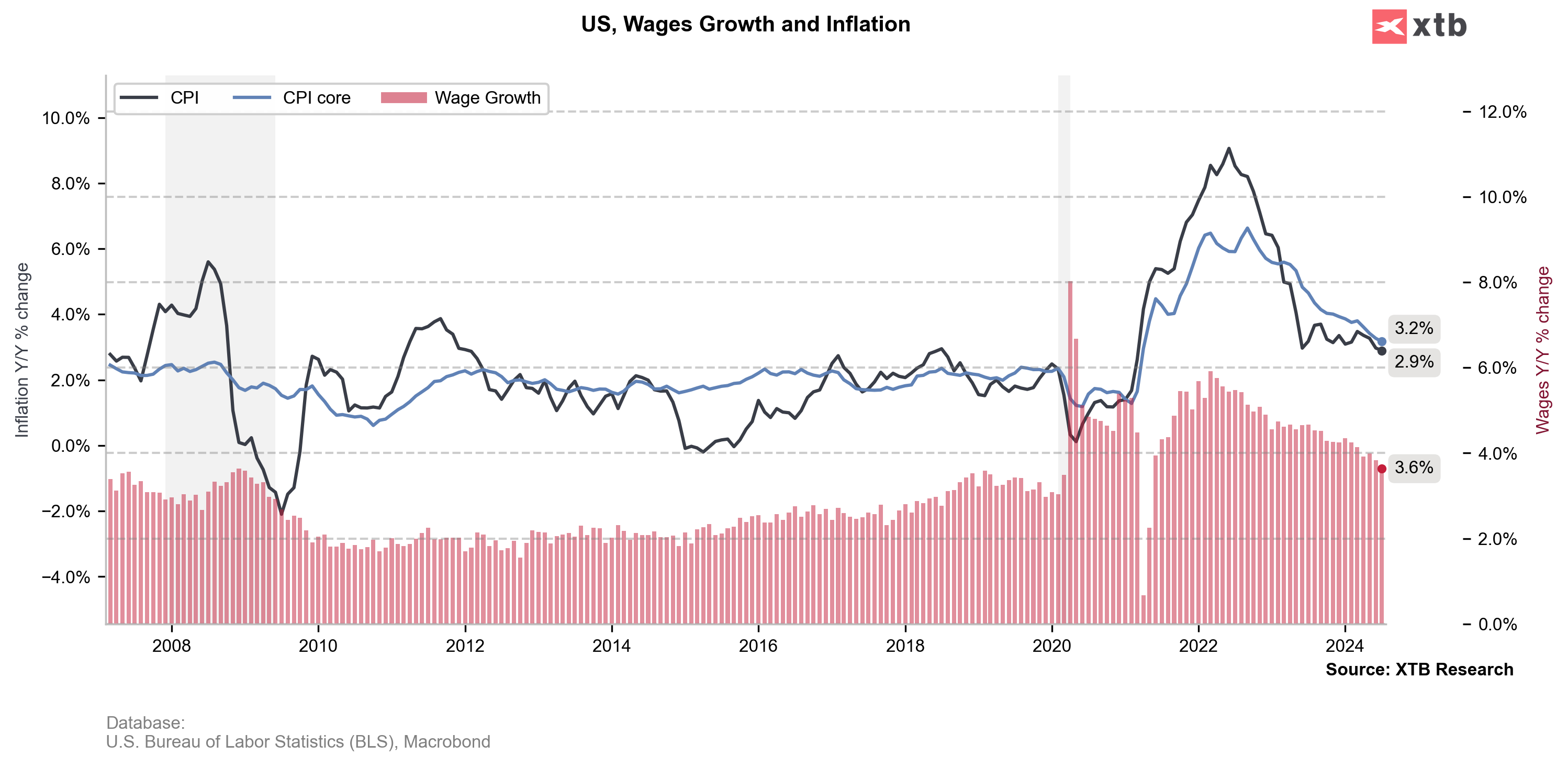
Wage growth is now at its lowest rate since 2021. Source: Bloomberg Finance LP, XTB
The market is pricing in strong cuts from the Fed
The market still sees a roughly 34% probability for a 50 basis point interest rate cut at the Fed's September meeting. In contrast, it is pricing in more than 4 cuts by the end of this year (the market sees a 60% probability for 5 cuts this year). It still seems that the baseline scenario for the Fed is a 25 basis point cut, although the labor market is sending some worrying signals. If inflation - especially core inflation - showed a clear slowdown for August, the likelihood of a 50-bp cut for September cannot be ruled out, which could weaken the dollar. Inflation in line with expectations or a rebound in core inflation could rule out larger cuts at the next FOMC meeting.

The market is pricing in cuts of about 250-260 basis points by early 2026. Source: Bloomberg FInance LP
How will the market react?
EURUSD is clearly rebounding after the declines earlier this week. Of course, the dollar's weakness can also be linked to the market's reaction to the results of the US presidential debate. Nevertheless, lower-than-expected inflation could lead to further increases on the pair towards the 1.11 level. In turn, a rebound in core inflation, although unlikely, could send the pair to its lowest levels since mid-August and test the 1.10 level.
Source: xStation5

Chart of the Day: USD/JPY highly volatile ahead of US CPI

Economic calendar: US CPI in the spotlight (13.02.2026)

Morning Wrap: Global sell-off in the technology sector (13.02.2026)

Daily summary: Silver plunges 9% 🚨Indices, crypto and precious metals under pressure